Overview of Biopsychology:
History of Biopsychology:
Perspective of brain and Behavior:
Biological factors that may influenced human Behavior:
Difference between brain and Mind:
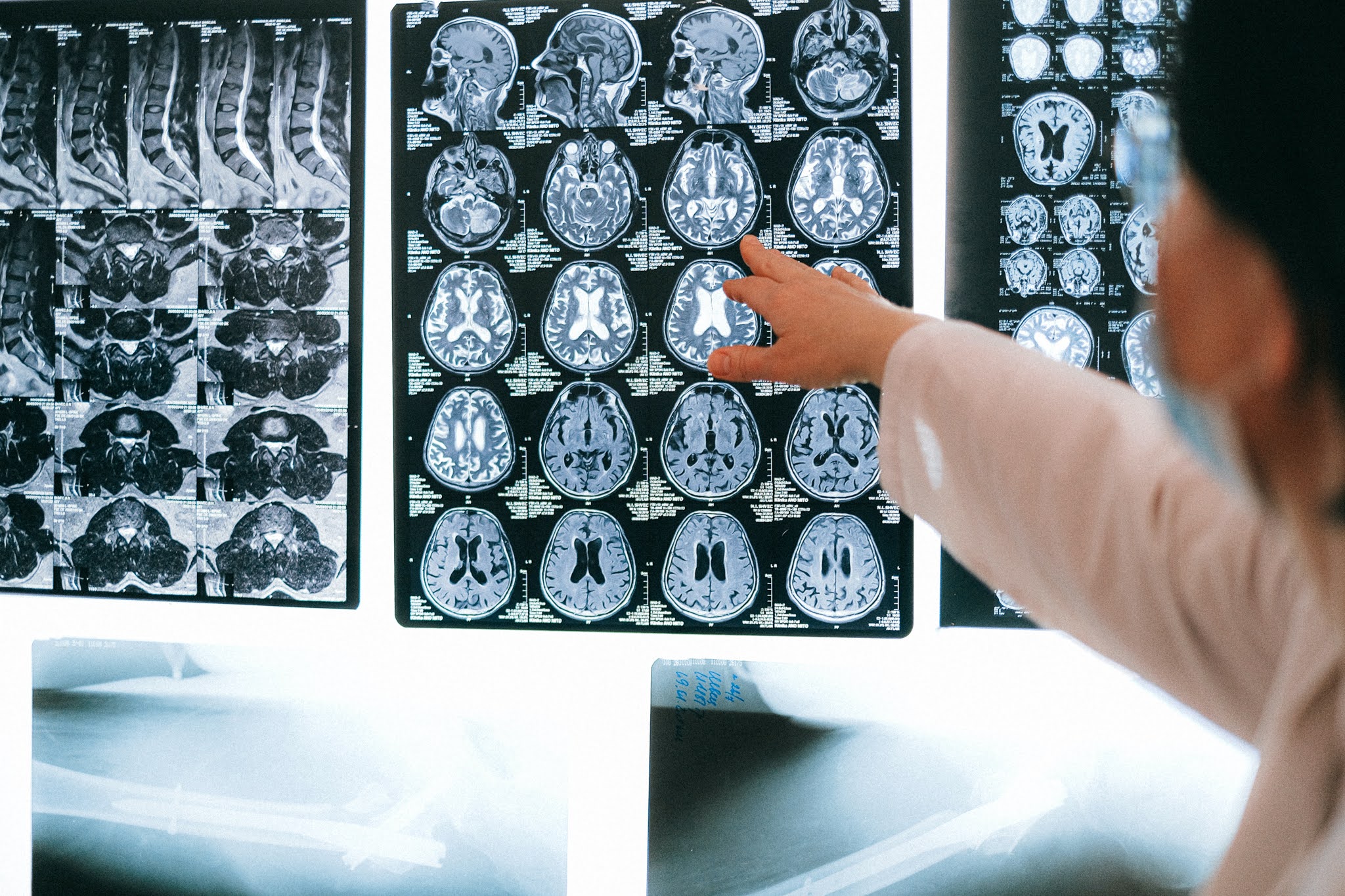
Method of Studying human Brain:
Several methods are used to study the human brain. The clinical/anatomical method involves studying the central nervous system of a patient who has suffered brain damage due to an injury. Invasive methods, such as chemical or electrical stimulation of the brain, are used only for non-human animals. The electroencephalogram (EEG) technique is used to measure the electrical activity of the brain, which is recorded from the outside by fitting electrodes to the skull. The activities of the brain can be traced on paper, and typically, brainwave patterns are associated with different states of arousal. Computed tomography (CT) scanning is used primarily for the detection and diagnosis of brain injuries and diseases. Positron emission tomography (PET) diagnoses brain abnormalities more efficiently than CT. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used to identify small tumors in the brain and the slightest reduction of blood flow in veins. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) are methods used to focus on the tiny area of the brain.
Evolution of Brain and Behavior:
How nerves system influence our Behavior:
The nervous system is a complex network of cells and organs that coordinate and control the functions of the body. It is responsible for receiving information from the environment, processing it, and generating appropriate responses.
The nervous system can be divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, which are enclosed and protected by the bones of the skull and vertebral column, respectively. The PNS includes all the nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body, including the cranial nerves that originate from the brain and the spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord.
The nervous system is composed of two types of cells: neurons and glial cells. Neurons are specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. They have a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals from other neurons), and an axon (which sends signals to other neurons). Glial cells, on the other hand, provide support and insulation for neurons, and play important roles in regulating the environment around neurons.
The nervous system uses electrical and chemical signals to communicate information between neurons. When a neuron receives a signal from another neuron, an electrical impulse called an action potential is generated, which travels down the axon and triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on other neurons, either exciting or inhibiting their activity, and allowing information to be transmitted throughout the nervous system.
The nervous system is involved in a wide range of functions, including sensation, movement, thought, emotion, and behavior. Disorders of the nervous system can have serious consequences, including paralysis, seizures, dementia, and mental illness. Treatments for nervous system disorders include medication, surgery, and various forms of therapy.
Neurotransmitters and Hormones:
Some important neurotransmitters and hormones involved in behavior are:
Dopamine:
Serotonin:
Oxytocin:
Testosterone:
Gut-Brain Axis:
The gut produces several hormones and neurotransmitters that can influence mood and behavior. For example, serotonin, which is produced in the gut, is involved in regulating mood, while ghrelin, which is produced in the stomach, is involved in regulating appetite.
The gut microbiome, which is the community of microorganisms that live in the gut, can also influence behavior. Studies have shown that changes in the gut microbiome can lead to changes in mood, cognition, and social behavior.
Genetics and Behavior:
Twin studies have been used to investigate the role of genetics in behavior. Identical twins share 100% of their genes, while fraternal twins share on average 50% of their genes. By comparing the behavior of identical twins to that of fraternal twins, researchers can estimate the heritability of a trait.








0 Comments